Heartbeat Monitors
Heartbeat monitors allow you to monitor systems using a "push" based approach, where your services send signals (or "heartbeats") to Kener on a regular basis. If Kener doesn't receive a heartbeat within the configured time period, it will mark the system as degraded or down.
This is useful for monitoring services that:
- Run on a schedule
- Cannot be directly accessed for pull-based monitoring
- Need to report their own health status
How It Works
- You configure a heartbeat monitor in Kener
- Kener provides a unique URL endpoint for your service to ping
- Your service sends HTTP requests to this endpoint at regular intervals
- If Kener doesn't receive a ping within the configured time window, it will mark the service as degraded or down
Setting Up a Heartbeat Monitor
To create a heartbeat monitor:
- Navigate to the Monitors page in the dashboard
- Click "Add Monitor"
- Select "Heartbeat" as the monitor type
- Configure the following settings:
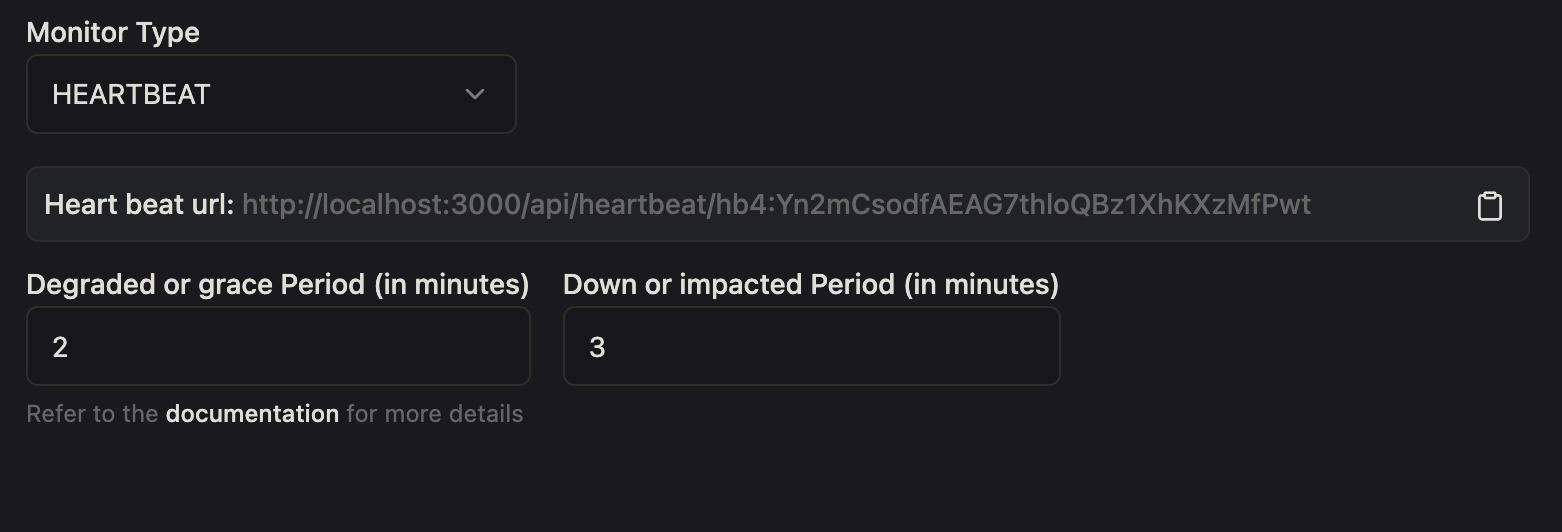
Configuration Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Secret String | A unique secret that authenticates your heartbeat requests |
| Degraded After (Minutes) | Number of minutes after which the service is considered degraded if no heartbeat is received |
| Down After (Minutes) | Number of minutes after which the service is considered down if no heartbeat is received |
Sending Heartbeats
Your service needs to send HTTP requests to the Kener heartbeat URL. Both GET and POST requests are supported.
Endpoint Format
https://<your-kener-instance>/api/heartbeat/<tag>:<secretString>
Where:
<tag>is the tag you configured for your monitor<secretString>is the secret you configured during setup
Example
If your monitor has:
- Tag:
nightly-backup - Secret String:
super-secret-key
Your service should send requests to:
https://<your-kener-instance>/api/heartbeat/nightly-backup:super-secret-key
You can use any HTTP client to send these requests, such as curl:
curl https://<your-kener-instance>/api/heartbeat/nightly-backup:super-secret-key
Or in a scheduled script:
#!/bin/bash
# Run your task here
./perform-backup.sh
# Send heartbeat to Kener
curl https://<your-kener-instance>/api/heartbeat/nightly-backup:super-secret-key
Monitoring State
The monitor status works as follows:
- UP: Heartbeats are being received within the configured time windows
- DEGRADED: No heartbeat has been received for longer than the "Degraded After" time period
- DOWN: No heartbeat has been received for longer than the "Down After" time period
Security Considerations
- Keep your secret string confidential, as anyone with knowledge of it can send heartbeats
- Consider using HTTPS for your Kener instance to encrypt heartbeat communications
- Rotate the secret string periodically by updating the monitor configuration
Best Practices
- Set the "Degraded After" time slightly longer than your expected interval between heartbeats
- Set the "Down After" time based on your SLA requirements
- For critical systems, consider sending heartbeats more frequently than required
- Add logging in your service to track successful and failed heartbeat attempts
Heartbeat monitors provide a simple but effective way to ensure your scheduled tasks and services are running properly, without requiring external polling.